Wikipedia
This text was copied from Wikipedia on 15 December 2024 at 6:10AM.
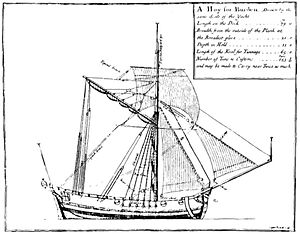
A hoy is a small Gaff-rigged coasting ship or a heavy barge used for freight, usually with a burthen of about 60 tons (bm). The word derives from the Middle Dutch hoey. In 1495, one of the Paston Letters included the phrase, An hoye of Dorderycht (a hoy of Dordrecht),[2] in such a way as to indicate that such contact was then no more than mildly unusual. The English term was first used on the Dutch Heude-ships that entered service with the Royal Navy.
Evolution and use

Over time the hoy evolved in terms of its design and use. In the fifteenth century a hoy might be a small spritsail-rigged warship like a cromster. Like the earlier forms of the French chaloupe, it could be a heavy and unseaworthy harbour boat or a small coastal sailing vessel (latterly, the chaloupe was a pulling cutter – nowadays motorized). In the sixteenth century, Sir Roger Williams considered that a combination of manoeuvrability, shallow draught, and heavy artillery made the hoy the most effective warship in Dutch coastal waters.[3] Hoys played a significant role in the Siege of Sluis (1587).[4]
By the 18th and 19th Century hoys were sloop-rigged and the mainsail could be fitted with or without a boom. English hoys tended to be single-masted, whereas Dutch hoys had two masts. Principally, and more so latterly, the hoy was a passenger or cargo boat. For the English, a hoy was a ship working in the Thames Estuary and southern North Sea in the manner of the Thames sailing barge of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. In the Netherlands a slightly different vessel did the same sort of work in similar waters. Before the development of steam engines, the passage of boats in places like the Thames estuary and the estuaries of the Netherlands, required the skillful use of tides as much as of the wind.
Hoys also would carry cargo or passengers to the larger ships anchored in the Thames. The British East India Company used hoys as lighters for larger ships that could not travel up the Thames to London. These were commonly referred to as East India hoys.
In the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, English hoys plied a trade between London and the north Kent coast that enabled middle class Londoners to escape the city for the more rural air of Margate, for example.[5] Others sailed between London and Southampton. These were known as Margate or Southampton hoys and one could hail them from the shore to pick up goods and passengers.
The introduction of the early steamers greatly expanded this sort of trade. At the same time, barges were taking over the cargo coasting trade on the short routes. Together, these developments meant that hoys fell out of use.
Royal Navy

The British Royal Navy used hoys that were specially built to carry fresh water, gunpowder, or ballast. Some were employed in such tasks as laying buoys or survey work, while others served to escort coastal convoys. Still others were in the Revenue Service.
In 1793–94 the Royal Navy purchased 19 Dutch hoys as coastal gun-vessels, particularly for service under Admiral Sir Sidney Smith. In naval service these had 30-man crews and each carried one 24-pounder gun and three 32-pounder carronades.[6] Examples include HMS Scourge and HMS Shark (Shark's crew mutinied in 1795 and handed her over to the French). Around the end of the French Revolutionary Wars, the Navy sold its remaining armed hoys.
Concern about a possible French invasion led the Royal Navy on 28 September 1804 to arm 16 hoys at Margate for the defense of the coast. One of these bore the name King George. The Navy manned each hoy with a captain and nine men from the Sea Fencibles.[7] The same concern also led the British to build over a hundred Martello towers along the British and Irish coasts.
Because most hoys were merchantmen, they were also frequently taken as prizes during time of war. Many of the hoys in British naval service had been captured from enemies. One of the earliest on record was the Mary Grace, captured in 1522 and listed until 1525.
See also
- On the French coast, a similar but generally faster vessel type, which continued its development until later, was known as the chasse-marée. Its centre of operations was the Breton coast and it specialized in carrying fresh sea fish to market. It was normally rigged as a three-masted lugger.
Footnotes
- ^ Sutherland (1717), facing p. 17.
- ^ "The Paston Letters". archive.org. Retrieved 16 December 2019.
- ^ G Gascoigne, A Hundred Sundrie Flowers (Oxford 2000) p. 720
- ^ G Mattingley, The Defeat of the Spanish Armada (Penguin) p. 158 and p. 152
- ^ Whyman (1993).
- ^ Winfield (2008), pp. 324–5.
- ^ The Naval chronicle, Volume 12, p.329,
References
- Sutherland, William (1717), Britain's Glory, or Shipbuilding Unvail'd, Clarke, OCLC 731314497
- Whyman, John (1993), "The significance of the hoy to Margate's early growth as a seaside resort" (PDF), Archaeologia Cantiana, 111: 17–41, ISSN 0066-5894, archived (PDF) from the original on 3 June 2015, retrieved 3 June 2015
- Winfield, Rif (2008). British Warships in the Age of Sail 1793–1817: Design, Construction, Careers and Fates. Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-246-7.
Gallery
-
East Indiaman and hoys off Dordrecht, Aelbert Cuyp, (17th century)
-
Shipping off Woolwich, Thomas Mellish, 1748, National Maritime Museum. The vessel in the left foreground is a hoy.


9 Annotations
First Reading
vicente • Link
Hoy: a small sloop rigged coasting ship also a heavy barge for bulky cargo. [md hoei me,fr] of course- " a hoy there" and a "hoyden" for lout or better yet, a girl or women of the saucy kind
then Lambs essay for later.
"Can I forget thee, thou old Margate Hoy, with thy weatherbeaten, sun-burnt captain, and his rough accommodation "
later by charles lamb 1775-1834
http://www.angelfire.com/nv/mf/el…
vicente • Link
Hoy : "...A two-decker on the far left and a hoy in the right foreground both cross the picture plane in starboard-broadside view. Any smaller sailing craft can be seen closer inshore...."
http://www.nmm.ac.uk/mag/pages/mn…
hoy in painting see
http://www.cichw.net/pmscottlee.h…
nice ships of the
Mary • Link
Earliest reference to a hoy in English
comes in the Paston Letters (1495) "an hoy of Dorderyght" (Dordrecht).
vicente • Link
many references to the Margate hoy:
The sailing hoys, regularly plying their trade between Margate and London with their cargoes of vegetables, barley and fish, made Margate into one of the first seaside resorts. The privileged classes of the day adored Margate for its safe stretches of sand, temperate climate and close proximity to London. It used to take up to ten hours to reach Margate from London in a sailing hoy.
http://www.cinqueports.org/margat…
a hoy is a small vessel, usually rigged as a sloop, employed in carrying passengers and goods short distances along the seacoast
http://www.mapageweb.umontreal.ca…
So packed up all my little odds and ends,
Took silent leave of all my Margate friends,
And sought a gallant Vessel
vicente • Link
Hoy appears to be a coastal/river one masted ship for moving goods and Humans locally: see painting .
http://www.nmm.ac.uk/mag/pages/mn…
A famous one appears to the one that connected London to Margate, [Margate Hoy, see Lamb] there were others for the other Cinque ports, then the goods and people were transferred to cross channel vessels and then ferried to the Continent.
Greeting of another ship, From Sams book of Seamans Grammar:
in Aqua Scripto • Link
Hoy: The Dutch had a {Brezzan} Hoy
Lenght 48', Beam 14' Depth 5 foot 30 tons with single mast, Gaft rigged with Stay sail, Headsail and Spirit sail.
my take: The Word 'hoy' be Spanish meaning day, be applied to a boat that would be only used in day light hours, i.e. a day boat. Then became general usage for boats that be scared of the dark, like we use the word hoover etc.
another missing ref http://www.pepysdiary.com/diary/1…
dirk • Link
"hoy" be Spanish meaning day...
Not exactly. "Hoy" (from the Latin "hodie") means "today". "Day" in Spanish is "día".
in Aqua Scripto • Link
hoy; adv. - este dia, now {aday} It be like the English misusing Char {lady} for T, Te, Tea, Tay, chai, to wash the tea cups, as there be no love lossed with The Spanish at that time, in my petite mind it make sense to misuse the superiors word in a rather bad way.
As the boat be only used for day travel [now].
Second Reading
Bill • Link
HOY, a small Bark.
---An Universal Etymological English Dictionary. N. Bailey, 1675.